Information
Comparison of the difference between YJV and BVV cables
Release time: 2025-01-23
Comparison between YJV and BVV Cables
(I) Voltage Rating Differences
- The voltage rating of BVV cables is typically 300/500V, belonging to the category of low - voltage cables. This relatively low voltage rating determines that it is mainly suitable for some occasions with low voltage requirements, such as electrical connections in homes, lighting and power supply for ordinary electrical appliances in small commercial places. In homes, from lamps to various household appliances like TVs, refrigerators, and washing machines, their operating voltage is generally around 220V, and BVV cables can meet the power transmission requirements of these devices.
- YJV cables, on the other hand, have a wider range of voltage ratings. Common ones include low - voltage 0.6/1KV, medium - voltage 6/10KV, and high - voltage 26/35KV, etc. Among them, low - voltage YJV cables can be used for internal power distribution in some small factories and low - voltage power supply systems in residential communities. Medium - voltage and high - voltage YJV cables play a crucial role in the power transmission and distribution links of urban power grids. They can efficiently transmit electrical energy from power plants or substations to various regions, meeting the electricity demands of users of different scales.
(II) Structural Differences
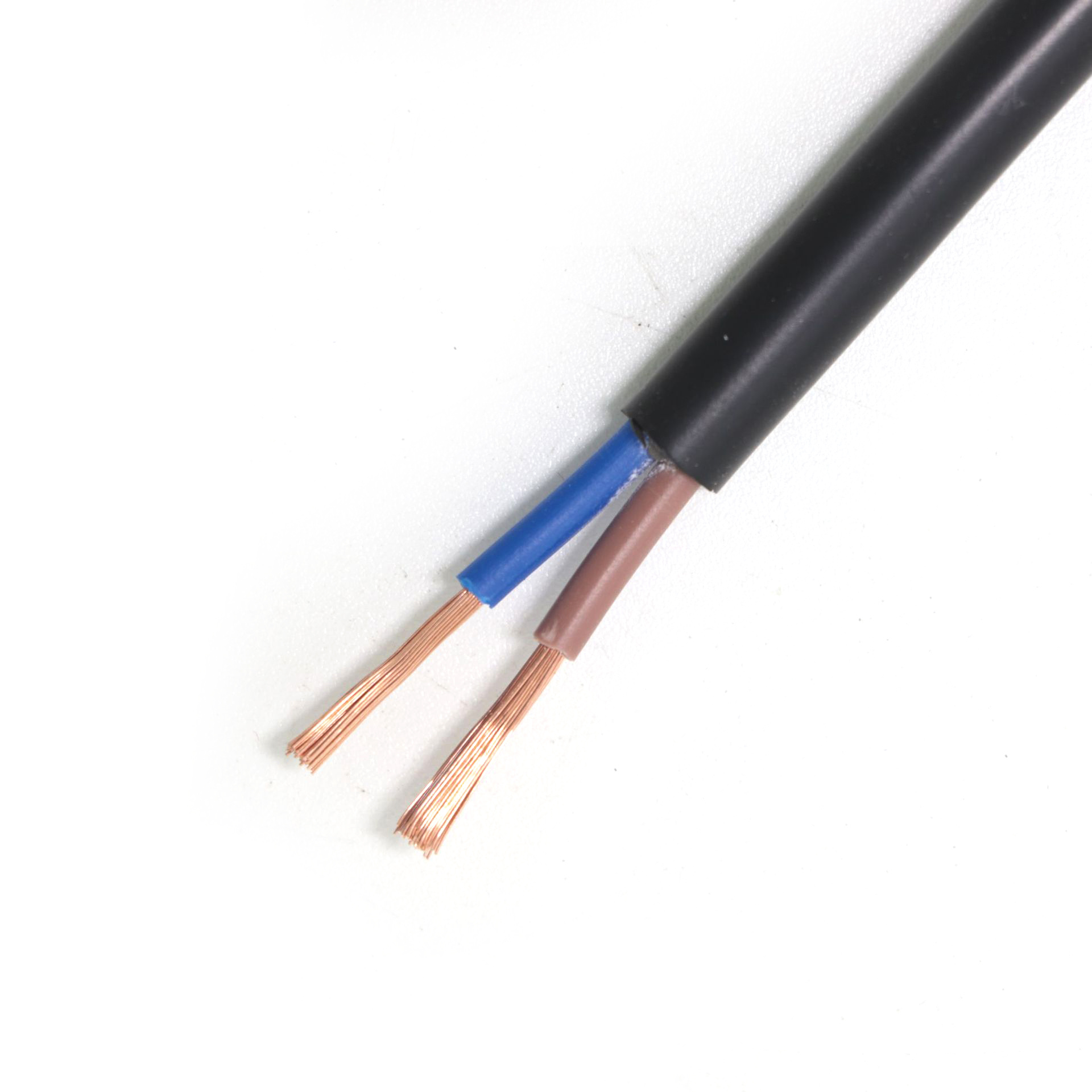
- Conductors: The conductors of BVV cables are usually single or multiple copper conductors. Common specifications include single - core, 2 - core, 3 - core, 4 - core, 5 - core, etc., and there are even various combinations such as 3 + 1, 3 + 2, 6 - core, and 7 - 24 - core. These conductors are closely arranged inside the cable to provide a path for power transmission. The conductors of YJV cables are also mainly made of copper or aluminum. Common conductor specifications include single - core, 2 - core, 3 - core, 4 - core, 5 - core, as well as combinations like 3 + 1, 3 + 2, 4 + 1. Compared with BVV cables, in some large - sized YJV cables, the conductors may adopt special stranding methods to improve the flexibility and current - carrying capacity of the cable. For example, in large - cross - section YJV cables, the conductors may adopt compacted circular or sector - shaped structures to reduce the gaps between conductors, lower the resistance, and improve the power transmission efficiency.
- Insulation Layer: The insulation layer of BVV cables is made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) material. This material has good insulating properties, which can effectively isolate the current and prevent electric leakage. At the same time, it also has a certain mechanical strength to protect the conductors from minor external forces. However, the insulating properties of PVC may decline in harsh environments such as high temperature and high humidity. The insulation layer of YJV cables is cross - linked polyethylene (XLPE), a polyethylene material that has undergone special treatment. Through the cross - linking reaction, its molecular structure changes from linear to three - dimensional network, greatly improving the insulating properties. XLPE has a low dielectric constant and small dielectric loss, which can effectively reduce the power loss during power transmission. It also has better heat resistance and chemical stability and can maintain good insulating properties under a wider range of environmental conditions.
- Sheath: The sheath of BVV cables is also made of PVC material. It has good abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, and moisture resistance, providing reliable external protection for the cable. In daily use, it can effectively resist external friction, collisions, and the erosion of chemical substances, ensuring the safe operation of the cable. The sheath of YJV cables is made of PVC. It has high mechanical strength to protect the internal structure of the cable from mechanical damage. At the same time, it also has good weather resistance and can adapt to different natural environments. Whether in cold winters or hot summers, it can maintain stable performance.
(III) Performance Differences
- Electrical Performance: Due to the use of XLPE insulation, YJV cables have high insulation resistance, a low dielectric constant, and small dielectric loss, which can effectively reduce power loss during power transmission and have a higher power transmission efficiency. This advantage is particularly obvious in long - distance and large - capacity power transmission. For example, in the high - voltage transmission lines of urban power grids, the use of YJV cables can reduce line losses and improve the economic efficiency and reliability of power supply. The electrical performance of BVV cables is relatively weak. The insulation resistance and dielectric properties of its PVC insulation layer are inferior to those of XLPE, and the power loss during power transmission is relatively large. Therefore, it is more suitable for short - distance and small - power power transmission scenarios.
- Thermal Performance: The maximum rated operating temperature of the conductor of YJV cables can reach 90°C, and the maximum temperature during a short - circuit does not exceed 250°C for no more than 5 seconds. This allows it to operate stably in a relatively high - temperature environment, withstand a larger current load, and is suitable for power supply to high - power equipment and power transmission in high - temperature environments. For example, in some industrial plants, large - scale mechanical equipment generates a large amount of heat during operation, and YJV cables can meet the power demands of these devices. The long - term allowable operating temperature of BVV cables does not exceed 65°C. In high - temperature environments, its current - carrying capacity is greatly limited, and it is not suitable for long - time, high - power, and high - temperature power transmission scenarios. However, in normal - temperature environments, it can meet the daily electricity demands of ordinary families and general commercial places.
- Protection Performance: The PVC sheath of BVV cables gives it excellent resistance to acids and alkalis, oil resistance, moisture resistance, and mildew resistance. In some environments with a risk of chemical corrosion, such as the workshops of chemical plants and kitchens, BVV cables can effectively resist the erosion of acid and alkali substances and ensure stable power transmission. In humid basements, bathrooms, and other places, its moisture - resistant performance can also guarantee the safe operation of the cable. The sheath of YJV cables also has certain protection performance, but in terms of chemical corrosion resistance, BVV cables perform more prominently. YJV cables have a certain advantage in mechanical protection. Their structure is relatively more robust and can withstand a certain degree of external extrusion and tension.
(IV) Application Differences
- Applications of YJV Cables: Due to its good electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties, YJV cables are widely used in fields with high requirements for power transmission, such as urban power grids, mines, and factories. In urban power grids, it undertakes the task of power distribution from substations to various regions, ensuring the stable power supply of cities. In mines, facing harsh working environments, YJV cables can provide reliable power support for mining equipment, ventilation systems, etc. In factories, the stable operation of various large - scale production equipment relies on the efficient power transmission of YJV cables.
- Applications of BVV Cables: Due to its low voltage rating, good protection performance, and relatively simple structure, BVV cables are mainly used in fields such as interior decoration, household appliances, and lighting equipment. In home decoration, it is a common choice for lighting circuits and socket wiring, providing safe and stable power connections for lamps, TVs, air conditioners, and other electrical devices. In household appliances, as the power cord, BVV cables ensure the normal operation and safe use of the appliances. In terms of lighting equipment, whether it is indoor chandeliers, ceiling lamps, or outdoor street lamps and landscape lights, BVV cables can be competent for power transmission work, providing good lighting conditions for people.
(V) How to Select the Appropriate Cable
1. Selection Based on the Usage Scenario
- Home Environment: For internal wiring in homes, such as lighting circuits and socket connections, BVV cables can usually be given priority. Its protection performance is good, which can adapt to various environments in homes, and the price is relatively affordable. In areas such as kitchens and bathrooms, which are humid and may have oil stains, the moisture - resistant and oil - resistant properties of BVV cables can ensure the safe and stable operation of the wires. However, for areas where high - power electrical appliances are concentrated, such as the power supply for central air - conditioners and instant - heating electric water heaters in villas, if the distance from the distribution box is long, considering the power loss during long - distance transmission and the current - carrying capacity requirements, low - voltage YJV cables can be selected to ensure the stable and reliable power supply.
- Factory Environment: There are many devices in factories, with high power consumption and extremely high requirements for power stability. YJV cables are suitable for power transmission and distribution inside factories due to their ability to withstand high operating temperatures, good electrical and mechanical properties. For large - scale production equipment, such as large - scale machine tools and injection molding machines, appropriate specifications of YJV cables should be selected according to the power and voltage requirements of the equipment. In some workshops with a risk of chemical corrosion, such as electroplating workshops and chemical raw material processing workshops, in addition to considering the corrosion resistance of YJV cables, YJV cables with special protective coatings can also be selected to further enhance their corrosion resistance.
- Outdoor Environment: In outdoor overhead lines or buried power lines, YJV cables are an ideal choice. Their good weather resistance and mechanical strength can withstand the erosion of natural environments such as wind, sunlight, and rain, as well as the pressure and humidity of underground soil. For example, in the urban street - lamp lighting system, YJV cables can stably transmit electrical energy to each street lamp, ensuring the normal operation of night lighting. In the construction of power transmission lines in some remote areas, YJV cables are widely used because they can adapt to complex geographical environments and harsh climate conditions. For some temporary outdoor power - using scenarios, such as the temporary power supply at construction sites, appropriate specifications of YJV cables or BVV cables can be selected according to the actual power - using requirements and distance. If the power - using equipment has a small power and is close to the distribution box, BVV cables can also meet the requirements; if the power is large or the distance is long, YJV cables should be given priority.
2. Selection Based on Electrical Requirements
- Voltage Requirements: Clearly defining the operating voltage of the electrical equipment is the key to selecting the cable. If the operating voltage of the equipment is within the range of 300/500V, BVV cables can basically meet the requirements. For ordinary household appliances such as TVs, refrigerators, and washing machines, their operating voltage is generally 220V, and BVV cables can be used. For equipment or power systems with an operating voltage of 0.6/1KV and above, such as high - voltage equipment in factories and power transmission and distribution lines in urban power grids, YJV cables need to be selected. For example, in a newly built industrial park, the power transmission between the internal high - voltage distribution room and each factory requires the use of YJV cables with a voltage rating of 0.6/1KV and above to ensure the safe and efficient transmission of high - voltage electrical energy.
- Current and Power: Calculate the required current value according to the power of the electrical equipment, and then select the appropriate cable specification according to the current - carrying capacity of the cable. Generally, the larger the power, the larger the required current, and a cable with a larger cross - sectional area should be selected. For small household appliances such as table lamps and fans, the power is small, and BVV cables with a cross - sectional area of 1.5 square millimeters or 2.5 square millimeters can be used. For equipment with a relatively large power, such as a 3 - horsepower air conditioner with a power of about 2.2kW and an operating current of about 10A, a cable with a cross - sectional area of 4 square millimeters or more should be selected. If YJV cables are selected, due to their relatively large current - carrying capacity, under the same power and current conditions, a slightly smaller - sized product than BVV cables can be selected, but accurate calculations and selections still need to be made according to specific electrical parameters and usage environments. In some large factories, the power of large - scale motors can reach tens of kilowatts or even hundreds of kilowatts. At this time, appropriate specifications of YJV cables need to be selected according to the rated power, rated current, and starting current of the motors to ensure that the motors can obtain stable power supply during startup and operation.
 oversea@hichain.com.cn
oversea@hichain.com.cn
 +8617328576881
+8617328576881