Information
YJV and BVV Cable Selection Guide (Part 1)
Release time: 2025-01-22
Among the many types of cables,YJVcables andBVVcables are widely used, and they have many differences in appearance, structure, performance, and application. Understanding these differences is of great significance for the planning, design, construction of power engineering, and the safety of daily household electricity. Whether it is electrical engineers choosing suitable cables for laying power grids, or decorators wiring homes, or ordinary consumers ensuring the safety of household electricity, masteringYJVthe differences betweenBVVcables can help them make more informed decisions and ensure the stability and safety of power transmission.
2.Comprehensive Analysis of YJV Cables
(1) Definition and Structure
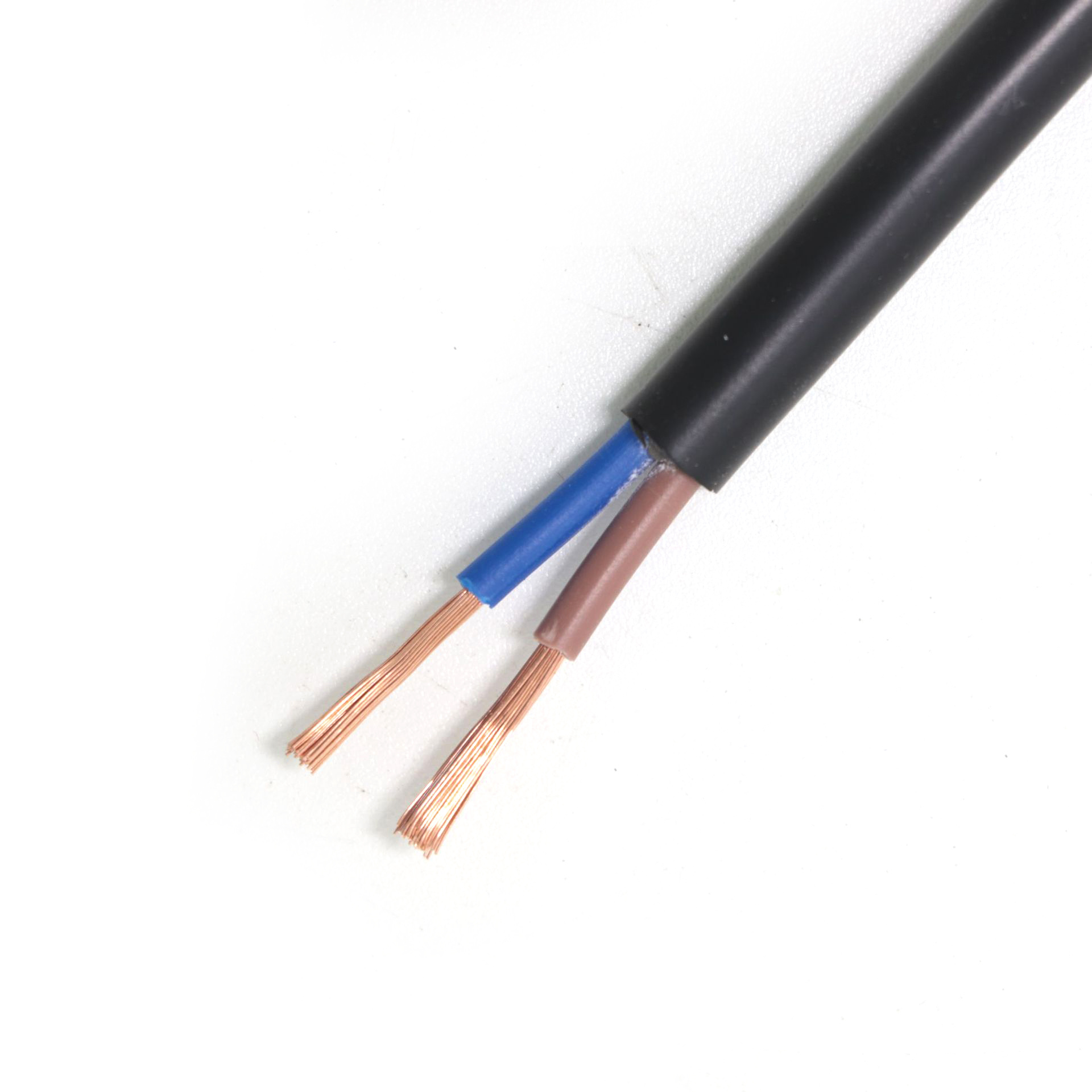
YJVThe full name of the cable is cross-linked polyethylene insulated polyvinyl chloride sheathed power cable. From the inside out, its structure mainly consists of a conductor, insulation layer, and sheath layer.
The conductor is usually made of high-purity copper or aluminum, with copper having good conductivity, ductility, and corrosion resistance, ensuring efficient current transmission. The insulation layer uses cross-linked polyethylene material, which transforms linear polyethylene molecules into a three-dimensional network structure through chemical or physical methods, significantly enhancing the thermal and electrical performance of polyethylene, effectively ensuring insulation between the conductor and the outside world. The outermost polyvinyl chloride sheath has high mechanical strength and chemical corrosion resistance, providing reliable protection for the internal structure of the cable and preventing external factors from causing damage.
(2) Performance Characteristics
- Electrical Performance:The dielectric constant of the cross-linked polyethylene insulation layer is low, with small dielectric loss and high insulation resistance, effectively reducing energy loss during transmission, ensuring the stability and reliability of power transmission, and lowering safety risks caused by leakage and other issues.
- Thermal Performance:The maximum rated operating temperature of the conductor can reach 90°C, which allows it to operate stably at higher temperatures compared to some other types of cables, permitting a larger current-carrying capacity to meet high-power transmission needs. At the same time, during a short circuit, the maximum temperature of the conductor does not exceed250°C, and the duration does not exceed5seconds, allowing it to withstand short-circuit current impacts for a certain period, protecting the safety of the power system.
- Mechanical Performance:The structure is stable, lightweight, and has a small outer diameter, making it easy to lay and install. Its small bending radius can adapt to complex laying environments, reducing construction difficulty and costs. It has obvious advantages when passing through narrow spaces such as buildings and tunnels.
(3) Common Specifications
YJVCommon core specifications of cables include single-core,2core,3core,4core,5core, and3+1,3+2,4+1and other combinations. The cross-sectional area ranges from1.0square millimeters to400square millimeters, such as1.5square millimeters and2.5square millimeters and4square millimeters commonly used for household lighting circuits;10square millimeters and16square millimeters and25square millimeters can be used for power supply in small commercial places or industrial equipment; while in large factories, urban power grids, and other high-voltage, high-power transmission scenarios, large specifications of cables of70square millimeters and95square millimeters and120square millimeters and above are often used.
(4) Application Fields
- Urban Power Grid:In the underground cable laying projects of cities,YJVYJV cables are widely used in high-voltage transmission lines and low-voltage distribution lines due to their good electrical performance, mechanical performance, and environmental resistance. They can stably deliver electrical energy from substations to various residential areas, commercial zones, and industrial parks, ensuring the normal operation of the city.
- Mining:The mining environment is harsh, with risks of humidity, corrosive gases, and mechanical collisions.YJVThe structure of the cable is robust, and the insulation and sheath materials have good corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, allowing them to adapt to the complex environment of mines, providing stable power supply for mining equipment, ventilation systems, lighting facilities, etc.
- Factories:There are many production devices in factories, which have extremely high requirements for the stability and reliability of power.YJVCables can provide suitable specifications for power transmission according to the power requirements of different devices, meeting the power needs of factory production. In automobile manufacturing factories, from automated production lines to various large machinery, they rely onYJVcables to provide stable power support.
3.In-depth Analysis of BVV Cables
(1) Definition and Structure
BVVThe full name of the cable is copper core polyvinyl chloride insulated polyvinyl chloride sheathed round cable, which belongs to the category of wiring cables. Its conductor is made of high-purity copper, ensuring good conductivity. The conductor is wrapped with a layer of polyvinyl chloride insulation, which not only effectively isolates the current to prevent leakage but also has certain mechanical strength to protect the conductor from minor external damage. The outermost polyvinyl chloride sheath further enhances the cable's protective capabilities, giving it good wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and moisture resistance. Compared toYJVYJV cables,BVVthe structure ofYJVBVV cables is relatively simple, lacking the complex chemical structure of cross-linked polyethylene in YJV cables, but it can exert its unique advantages in some low-voltage, short-distance power transmission scenarios.
(2) Performance Characteristics
- Protection Performance:It has excellent resistance to acids and alkalis, oil resistance, moisture resistance, and mildew resistance. In environments with chemical corrosion risks, such as workshops in chemical plants and kitchens,BVVthe cable can effectively resist the erosion of acidic and alkaline substances, ensuring stable power transmission. In humid places like basements and bathrooms, its moisture resistance can also ensure the safe operation of the cable, reducing risks of short circuits and leakage caused by humidity.
- Working Temperature:The long-term allowable working temperature does not exceed 65℃. Compared toYJVcables, its upper limit of working temperature is lower. This means that in high-temperature environments,BVVthe current-carrying capacity of the cable will be somewhat limited, making it unsuitable for long-term, high-power, and high-temperature power transmission scenarios. However, in normal temperature environments, such as ordinary households and general commercial places, it can meet daily power transmission needs.
- Safety:Obtained CCCcertification mark, indicating compliance with national safety standards. During the production process, there are strict requirements for the selection of raw materials, control of production processes, and quality testing of products, ensuring the safety and reliability of the product from the source. At the same time, its insulation and sheath materials have a certain degree of flame retardancy, which can delay the spread of fire in case of a fire, providing time for personnel evacuation and firefighting.
(3) Common Specifications
BVVCommon cross-sectional specifications of cables include0.75square millimeters and1square millimeters and1.5square millimeters and2.5square millimeters and4square millimeters and6square millimeters and10square millimeters and16square millimeters and25square millimeters, etc. Among them,0.75square millimeters and1square millimeters and1.5square millimeters are commonly used for small electrical devices, such as table lamps, televisions, computers, etc.;2.5square millimeters and4square millimeters can meet the power needs of some slightly larger appliances, such as air conditioners and electric water heaters;6square millimeters and10square millimeters are suitable for household incoming lines or main lines in small commercial places;16square millimeters and25square millimeters and above specifications are generally used for powering larger equipment in industrial plants.
(4) Application Fields
- Indoor Decoration:In home decoration,BVVcables are widely used in lighting circuits, socket wiring, etc. Its hard wire characteristics make it easy to fix and lay during wiring, keeping the lines neat and beautiful. In areas such as living rooms and bedrooms,BVVcables can be used to connect lamps, sockets, televisions, air conditioners, and other electrical devices, providing stable power support for family life.
- Household Appliances:For various household appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, microwaves, etc.,BVVcables serve as power lines, ensuring safe and reliable power supply during normal operation of the appliances. Its good protective performance can effectively avoid damage to the cable caused by friction, collision, and other situations that may occur during daily use, thereby ensuring the service life and safety of household appliances.
- Lighting Equipment:Whether it is indoor chandeliers, ceiling lights, or outdoor street lights, landscape lights, and other lighting equipment,BVVcables can perform the task of power transmission. In outdoor lighting, its moisture resistance, mildew resistance, and weather resistance can adapt to different natural environments, ensuring the stable operation of the lighting system and providing good lighting conditions for people's nighttime travel and activities.
YJVcables andBVVCables each have their own characteristics in the field of power transmission, playing indispensable roles.YJVCables, with their excellent electrical performance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, have become the first choice for high-voltage, high-power power transmission, widely used in urban power grids, mines, factories, and other places that require stable and efficient power supply. Meanwhile,BVVcables, with their good protective performance, safety reliability, and moderate working temperature, have become the ideal choice for low-voltage, short-distance power transmission in indoor decoration, household appliances, and lighting equipment. Understanding the differences and characteristics of these two types of cables is an important prerequisite for electrical engineers, decorators, and ordinary consumers to ensure stable and safe power transmission. When choosing cables, one should consider the performance characteristics, specifications, and cost-effectiveness of the cables based on specific application scenarios and needs, in order to make the most optimized decision.
 oversea@hichain.com.cn
oversea@hichain.com.cn
 +8617328576881
+8617328576881